Treatments
Light therapy
Light therapy is used in dermatology for the treatment of skin disorders such as eczema, psoriasis and pruritus (itching). Light therapy has a very beneficial effect on these skin diseases and is well tolerated by patients.
Light therapy involves the use of UVA or UVB light. UVB is most commonly used, particularly to treat the entire body. Wetering Medical Centre uses UVB (TL01) therapy, the most advanced type of light therapy.
UVB has a very strong effect on the skin; it is the part of sunlight that causes sunburn. That is why, at the start of UVB therapy, very short exposure times (about thirty seconds) are used.
In total body treatment with UVB, you will be instructed to stand in a special cabinet with panels of fluorescent tubes to enable overall exposure of the body. The assistant will set the UVB cabinet to the correct dose and start treatment. The UVB cabinet is on a timer and will switch itself off. You can open the door at any time, if necessary.
The optimum exposure time is one that is just long enough not to cause you to burn. Exposure time is gradually increased during treatment. The maximum exposure time is usually no more than eight minutes. You will not need to take any medication during UVB therapy. UVB treatment is usually given two or three times weekly, depending on the disease and type of exposure. The entire treatment lasts between eight and sixteen weeks, depending on the result.
Excision
 Excision is the (surgical) removal of a skin disorder. This procedure is usually performed under local anaesthesia on an outpatient basis.
Excision is the (surgical) removal of a skin disorder. This procedure is usually performed under local anaesthesia on an outpatient basis.
It is suitable for patients with skin disorders which, according to the physician, can best be removed by means of minor surgery, such as cysts or moles, or some forms of skin cancer.
In most cases – particularly when skin cancer is suspected – the removed piece of skin is sent to a pathologist for examination. In case of skin cancer, the pathologist checks whether the edges of this piece of skin are free of tumour tissue and whether the excision was complete. In some cases, the findings may lead the pathologist to recommend a second excision.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
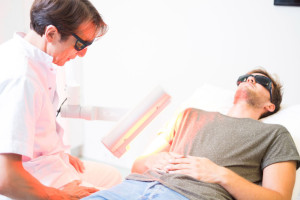 Photodynamic therapy is a method of treating localised skin abnormalities and cancers. The treatment consists of applying a special cream, Metvix, to the skin growth and 4 to 6 hours later shining a pure red light on it. The cream contains methyl aminolevulinate, which becomes active when exposed to light of a certain wavelength. This substance makes abnormal skin cells extra sensitive to light.
Photodynamic therapy is a method of treating localised skin abnormalities and cancers. The treatment consists of applying a special cream, Metvix, to the skin growth and 4 to 6 hours later shining a pure red light on it. The cream contains methyl aminolevulinate, which becomes active when exposed to light of a certain wavelength. This substance makes abnormal skin cells extra sensitive to light.
PDT can be used to treat certain types of skin cancer and pre-cancerous cells:
• Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), particularly the superficial variant
• Bowen’s disease (BD)
• Actinic keratosis (AK)
This therapy has the advantage that large skin areas can be treated without surgery. Moreover, the treatment reduces the risk of scarring.
Stikstofbehandeling (cryotherapie)
 Cryotherapy is a treatment in which the skin is frozen with the aid of liquid nitrogen. As a result, the abnormal skin dies off and is then replaced by new skin. After this treatment, a blister or scab develops on the skin, which takes about 1 to 2 weeks to heal. The underlying skin has often a light or pink colour. This is new, healthy skin that will slowly obtain a normal skin tone. This ‘new’ skin must be protected from the sun for six weeks.
Cryotherapy is a treatment in which the skin is frozen with the aid of liquid nitrogen. As a result, the abnormal skin dies off and is then replaced by new skin. After this treatment, a blister or scab develops on the skin, which takes about 1 to 2 weeks to heal. The underlying skin has often a light or pink colour. This is new, healthy skin that will slowly obtain a normal skin tone. This ‘new’ skin must be protected from the sun for six weeks.
Waiting time indication
Dermatology
Days
Gynaecology
Days
Proctology
Days
Phlebology
Days
Plastic surgery
Days




